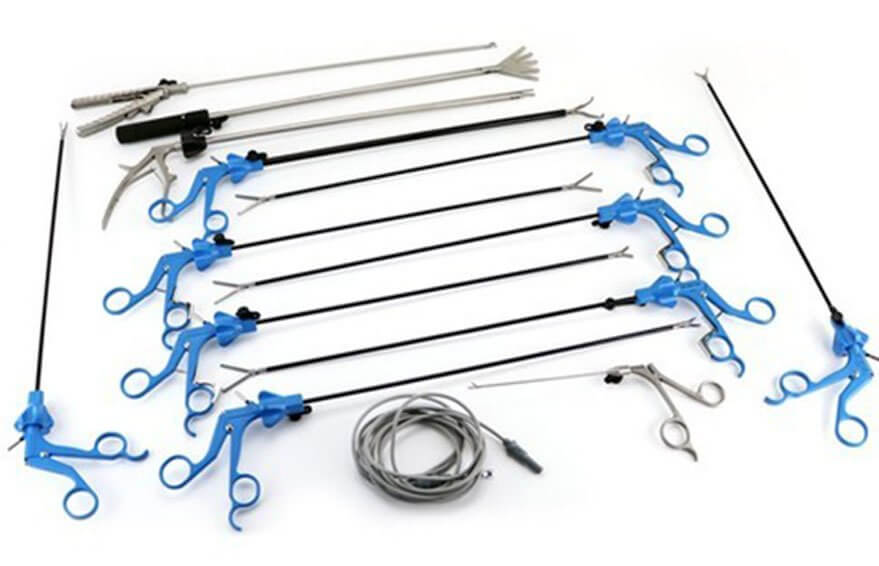
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations are performed far from their location through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) elsewhere in the body.
Three main Components:
Laparoscopic instrumentsØ Pneumoperitoneum Ø Image production
OPERATING ROOM SET-UP must include: A sufficient back up of instrumentation to cover for equipment failure. Facilities for intra-operative imaging. Dedicated interventional laparoscopic operating rooms. The proper hardware and instruments.
Laparoscopic instrumentation can be broadly devided as
-
Optical Devices
-
Equipment for creating / maintaining domain
-
Instruments for Access
-
Operative instruments
-
Energy sources
-
Tissue approximation/ hemostasis
-
Miscellaneous
- Optical Devices -Telescope
This endoscope is made of surgical stainless steel containing an optical lens train comprised of precisely aligned glass lenses and spacers (Rod lens system): Telescopes or laparoscopes come in various sizes 10mm, 5mm, 2-3mm ‘needlescopes’ and with various visualization capabilities such as zero degree forward viewing, 30 or 45 degree telescope, zero degree telescope with 6mm instrument channel(operating laparoscope)
Light source
White light illumination is provided from a high- intensity xenon,mercury, or halogen lamp and delivered via a fiberoptic bundle
Light cable
There are two types of cables 1. Fiberoptic cables are flexible but do not transmit a precise light spectrum. 2. Fluid cables transmit more light and a complete spectrum but are more rigid. Fluid cables require soaking for sterilization and cannot be gas sterilized.
Video Camera
The basis of laparoscopic cameras is the solid state silicon computer chip or CCD (charge-coupled device ). The resolution or clarity of the image depends upon the number of pixels or light receptors on the chip. Standard cameras in laparoscopic use contain 250,000 to 380,000 pixels.
Television Monitor
High-resolution video monitors are required for suitable reproduction of endoscopic image. Three chip cameras require monitors with 700 lines resolution to realize the improved resolution of extra chip sensors. VHS recorder, video printer and sometimes DVD recorder are standard documentation equipments housed in the video cart.
- Equipment for creating / maintaining domain
Gas insufflation
-
CO2 Insufflator: The creation of working space in the abdominal cavity is generally done using CO2 delivered via an automatic, high flow,pressure regulated insufflator. CO2 is currently the agent of choice due to low risk of gas embolism,low toxicity to peritoneal tissues, rapid reabsorption, low cost and inhibits combustion. The insufflator delives gas at a flow rate of up to 20 liters / min. Level is usually set at 12 to 15 mm Hg.
Gasless laparoscopy: This has some theoretical advantages in some high- risk patients with compromised cardio-respiratory function It facilitates continuous suction and use of some conventional open instruments.
- Instruments for Access Veress needle:
The Veress needle is designed to create pneumoperritoneum prior to insertion of trocar in a closed fashion. It consists of an outer sharp cutting needle and inner blunt spring-loaded obturator.
Hasson’s cannula:used for gaining initial access to the abdominal cavity with an open cutdown technique.
Optical trocar: allows visualization of the tissues as the blade cuts through the layers of the abdominal wall
- Operative Instruments :
Trocars: Available in various diameters and sizes according to requirements, 10mm and 5 mm being commonly used. Of the bladed trocars, there are shielded and nonshielded types.They are Bladed and nonbladed types.
Graspers: Retraction may be achieved using large grasping instruments.
Bullet Nose Grasper with either straight or diamond-cut serrations has a blunt bullet nose tip design with an atraumatic grasping jaw (one that will not produce tissue damage). These graspers are ideal for dissecting or grasping delicate anatomy. It is important to give attention to the cleaning of the jaw serrations and hinged areas of the instrument.
Dorsey Intestinal Fenestrated Grasper has atraumatic horizontal serrations.
Hunter Bowel Grasper has two rows of atraumatic serrations. The jaw comes in different lengths,depending on the needs of the surgical procedure.
Crocodile Grasper has long contoured jaws with tissue herniation channels to ensure superior grasping ability.
Raptor Grasper has long contoured jaws with tissue herniation channels. It also has two atraumatic teeth at the tip for grasping difficult anatomy.
Triangular Endo Flex Retractor (angled or straight) is used for retraction during large organ surgery. Two common lengths are 60mm and 80mm.
Dissectors
Maryland Dissector has long, curved jaws with fine- tapered tips. Ideal for precise dissection (resembles the Crile hemostatic clamp used in open surgeries). Bipolar Dissector consists of four pieces when disassembled, and it should be left disassembled during the sterilization cycle. At the sterile field, scrub personnel should assemble the dissector before use and attach a bipolar cord that delivers the electrosurgical energy to the instrument. It is used to achieve hemostasis.
Scissors There are a variety of scissors for dissecting, mobilizing and cutting tissues, which include straight and curved types (Endo Shears).Repeated use of diathermy at the sharp edge may tend to blunt the scissors. Hook scissors should always be kept in view while entering and exiting.
Bowel and lung clamp: Tubular structures, bowel and lung can be held with instruments designed specifically for the same. (Endo-Babcocks, Endo-Lung, Bowel Clamp).
- Energy Sources
Electrosurgery: Electrocautery refers to direct current whereas electrosurgery uses alternating current. During electrocautery, current does not enter the patient’s body. Only the heated wire comes in contact with tissue. In electrosurgery,the patient is included in the circuit and current enters the patient’s body.
Bipolar: In bipolar electrosurgery, both the active electrode and return electrode functions are performed at the site of surgery. The two tines of the forceps perform the active and return electrode functions. Only the tissue grasped is included in the electrical circuit.
Monopolar: The active electrode is in the wound. The patient return electrode is attached somewhere else on the patient. The current must flow through the patient to the patient return electrode to complete the circuit.
Safety Considerations during Electrosurgical laparoscopic surgery: there can be chances of- Insulation Failure:Capacitive Coupling: Direct Coupling:
Most potential problems can be avoided by following: · Inspect insulation carefully · Use lowest possible power setting · Use a low voltage waveform (cut) · Use brief intermittent activation vs. prolonged activation · Do not activate in close proximity or direct contact with another instrument · Use bipolar electrosurgery when appropriate · Select an all-metal cannula system as the safest choice .Do not use hybrid cannula systems that mix metal with plastic · Utilize available technology, such as a tissue response generator to reduce capacitive coupling or an active electrode monitoring system, to eliminate concerns about insulation failure and capacitive coupling.
Argon-Enhanced Electrosurgery incorporates a stream of argon gas to improve the surgical effectiveness of the electrosurgical current. Argon gas is inert and noncombustible making it a safe medium through which to pass electrosurgical current
Ultrasonic Energy: (The Harmonic scalpel) Uses ultrasonic technology, the unique energy form that allows both cutting and coagulation at the precise point of impact,resulting in minimal lateral thermal tissue damage. Cuts and coagulates by using lower temperatures than those used by electrosurgery or lasers. Coagulation occurs by means of protein denaturation when the blade, vibrating at 55,500 Hz, couples with protein, denaturing it to form a coagulum that seals small coapted vessels.It offers greater precision in tight spaces near vital structures,fewer instrument changes are needed, less tissue charring and desiccation occur, and visibility in the surgical field is improved.
- Instruments for Tissue approximation/ Hemostasis
- Laparoscopic ligating suture delivery system: A Pre-tied sliding knot with a loop is available with nylon carrier rod to ligate stump like structures or tubular structures after cutting. Eg Surgitie..The suture is looped around the structure to be ligated and the knot is slid down to close the loop. Useful in appendicectomy
- Needle drivers: Endostitch is a 10mm disposable suturing device. The needle features a sharp tapering point at each end with suture attachment at the center of the needle. The double-ended needle is passed between the two jaws of the suturing device. Its advantages include easy introduction, atraumatic needle manipulation, good security and easy accurate needle placement
- Clip Applicators: Clip appliers are primary modality for ligating blood vessels and other tubular structures. Disposable clip appliers contain up to 20 clips, whereas reusable clip appliers carry one clip at a time. Clips are made of titanium though now absorbable clips are also available.
Mechanical Stapling Instruments: A range of staple lengths (2.5-3.8mm)is available depending on the thickness of the tissue to be divided.Laparoscopic staplers are modifications of stapling devices of open surgery. Staplers are used for transecting and anastomosing bowel, transecting mesentery etc.
- Miscellaneous
Aspiration / Irrigation probes: These are essential for most laparoscopic procedures in order to maintain a clear operative field. Irrigation and aspiration channels may be incorporated into surgical instruments but working channels are small and subject to repeated clogging.
Hand Assisted Laparoscopic surgery: The Hand Access Device is intended to provide extracorporeal extension of pneumoperitoneum and abdominal access for the surgeon during laparoscopic surgery. It is indicated for use in laparoscopic procedures, where entry of the surgeon’s hand may facilitate the procedure, and for extraction of large specimens.
Organ Extraction devices: These are pre loaded specimen retrival pouches made of strong material, which is impervious to cancer cells. The mouth of the pouch is bought out of the incision site and opened following which the specimen is extracted
Tissue Morcellators: These are used to reduce the size of the resected specimen prior to retrieval Eg.Laparoscopic myomectomy. It may render pathological examination more difficult.
Dr. Pavithra